Easy Basics of ECG Learning is one the challenging for the medical students. While studying the medicine ECG is one of the important topic to master. ECG reading will be difficult if we don’t know the proper way or the basic . Here are some the basic things which can be easily reading the ECG .
ECG -Basics
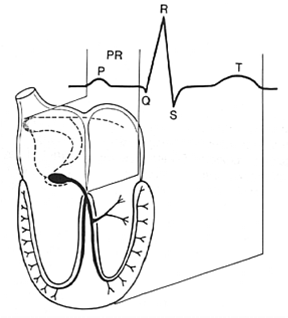
Normal Impulse Conduction
Sinoatrial node–AV node–Bundle of His–Bundle Branches–Purkinje fibers
The “PQRST”
► P wave – Atrial depolarization
QRS – Ventricular depolarization
T wave – Ventricular repolarization
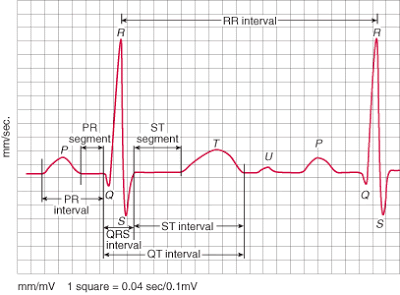
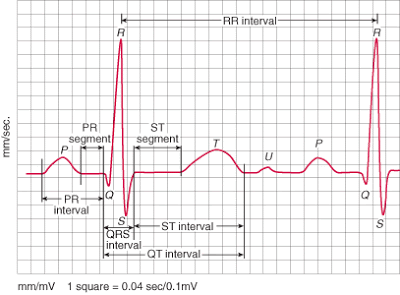
The PR Interval
Atrial depolarization
+
delay in AV junction
(AV node/Bundle of His)
(delay allows time for the atria to contract before the ventricles contract)
Pacemakers of the Heart
► SA Node – Dominant pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 60 – 100 beats/minute.
► AV Node – Back-up pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 40 – 60 beats/minute.
► Ventricular cells – Back-up pacemaker with an intrinsic rate of 20 – 45 bpm.
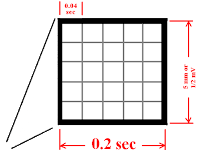
The ECG Paper
► Horizontally
One small box – 0.04 s
One large box – 0.20 s
► Vertically
One large box – 0.5 mV
► Every 3 seconds (15 large boxes) is marked by a vertical line.
► This helps when calculating the heart rate.
ECG 2 -How to Analyze a Rhythm
• Step 1: Calculate rate.
• Step 2: Determine regularity.
• Step 3: Assess the P waves.
• Step 4: Determine PR interval.
• Step 5: Determine QRS duration.
Step 1: Calculate Rate
• Option 1
– Count the # of R waves in a 6 second rhythm strip, then multiply by 10.
– Reminder: all rhythm strips in the Modules are 6 seconds in length.
Interpretation? 9 x 10 = 90 bpm
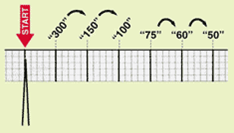
• Option 2
– Find a R wave that lands on a bold line.
– Count the # of large boxes to the next R wave. If the second R wave is 1 large box away the rate is 300, 2 boxes – 150, 3 boxes – 100, 4 boxes – 75, etc.
– Memorize the sequence:
300 – 150 – 100 – 75 – 60 – 50
Step 2: Determine regularity
• Look at the R-R distances (using a caliper or markings on a pen or paper).
• Regular (are they equidistant apart)? Occasionally irregular? Regularly irregular? Irregularly irregular?
Interpretation? Regular
Step 3: Assess the P waves
• Are there P waves?
• Do the P waves all look alike?
• Do the P waves occur at a regular rate?
• Is there one P wave before each QRS?
Interpretation? Normal P waves with 1 P wave for every QRS
Step 4: Determine PR interval
• Normal: 0.12 – 0.20 seconds.
(3 – 5 boxes)
Interpretation?0.12 seconds
Step 5: QRS duration
• Normal: 0.04 – 0.12 seconds.
(1 – 3 boxes)
Interpretation? 0.08 seconds
Rhythm Summary
• Rate 90-95 bpm
• Regularity regular
• P waves normal
• PR interval 0.12 s
• QRS duration 0.08 s
Interpretation? Normal Sinus Rhythm
ECG 3-Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
• Etiology: the electrical impulse is formed in the SA node and conducted normally.
• This is the normal rhythm of the heart; other rhythms that do not conduct via the typical pathway are called arrhythmias.
![]()
NSR Parameters
• Rate 60 – 100 bpm
• Regularity regular
• P waves normal
• PR interval 0.12 – 0.20 s
• QRS duration 0.04 – 0.12 s
Any deviation from above is sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia or an arrhythmia
Arrhythmia Formation
Arrhythmias can arise from problems in the:
• Sinus node
• Atrial cells
• AV junction
• Ventricular cells
SA Node Problems
The SA Node can:
fire too slow— Sinus Bradycardia
fire too fast— Sinus Tachycardia
Atrial Cell Problems
Atrial cells can:
• fire occasionally from a focus —Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)
• fire continuously due to a looping re-entrant circuit —-Atrial Flutter
Atrial Cell Problems
Atrial cells can also:
• fire continuously from multiple foci Atrial Fibrillation
or
fire continuously due to multiple micro re-entrant “wavelets” Atrial Fibrillation
AV Junctional Problems
The AV junction can:
• fire continuously due to a looping re-entrant circuit–Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
• block impulses coming from the SA Node–AV Junctional Blocks
Ventricular Cell Problems
Ventricular cells can:
• fire occasionally from 1 or more foci –Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
• fire continuously from multiple foci–Ventricular Fibrillation
• fire continuously due to a looping re-entrant circuit–Ventricular Tachycardia