List of Pathology Mnemonics collected from different websites
Pulmonary fibrosis: differential of both upper and lower lobes
BREAST SCAR:
· Upper lobe:
Beryliosis
Radiation
Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Sarcoidosis
TB
· Lower lobe:
Systemic sclerosis
Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis
Asbestosis
Radiation
Gout vs. pseudogout: crystal lab findings Pseduogout
crystals are:
Positive birefringent
Polygon shaped
· Gout therefore is the negative needle shaped crystals.
· Also, gout classically strikes great Toe, and its hallmark is Tophi.
Pulmonary embolism: risk factors 7 H’s:
Hereditary (eg factor V Leyden, protein C or S deficiency)
History (previous DVT or PE)
Hypomobility (fracture, CVA, severe illness, obesity, long trip)
Hypovolaemia (nephrotic syndrome, dehydration)
Hypercoagulability (smoking, malignancy)
Hormones (oestrogens [esp. in OCP], puerperium)
Hyperhomocysteinaemia
APKD: signs, complications, accelerators 11 B’s:
· Signs:
Bloody urine
Bilateral pain [vs. stones, which are usually unilateral pain]
Blood pressure up
Bigger kidneys
Bumps palpable
· Complications:
Berry aneurysm
Biliary cysts
Bicuspid valve [prolapse and other problems]
· Accelerators:
Boys
Blacks
Blood pressure high
Barter’s syndrome: pathogenesis, major sign Barter: “In
exchange for giving away Na+,K+,Cl-, you can drop the blood pressure”.
Thyrotoxicosis syndrome: signs and symptoms “A Penny
For Every Symptom That Hyperthyroidism Will
Make Grossly Evident”:
Anxiety
Palpitations/ Pulse rapid
Fatigability
Emotional lability
Sweating
Tremor
Heat intolerance
Weight loss with good appetite
Muscular weakness/ Menstrual changes
Goitre
Eye changes
Peptic ulcer: associated causative factors SHAZAM:
Smoking
Hypercalcemia
Aspirin
Zollinger-Ellison
Acidity
MEN type I
· These may work with H. pylori to promote ulceration, or may act alone.
Carcinoid syndrome: components CARCinoid:
Cutaneous flushing
Asthmatic wheezing
Right sided valvular heart lesions
Cramping and diarrhea
Anemia causes (simplified) ANEMIA:
Anemia of chronic disease
No folate or B12
Ethanol
Marrow failure & hemaglobinopathies
Iron deficient
Acute & chronic blood loss
Gynecomastia: causes DaLAS:
Digitalis
Leydig cell tumors
Alcohol
Sertoli cell tumors
Pick’s disease: location, action, epidemiology · See figure.
Pick axes are Picking away at the old woman’s cerebral cortex,
causing cortical atrophy.
2 pick axes on her brain: frontal lobe and anterior 1/3 of temporal.
An old woman, since epidemiology is elderly & more common in women.
Multiple sclerosis (MS): pathology MS attacks the
Myelin Sheath, resulting in plaques.
Nasopharyngeal malignant cancers NASOPharyngeal:
Nasophayngeal
Adenocarcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Olfactory neuroblastoma
Plasmacytoma
Acute ischemia: signs [especially limbs] 6 P’s:
Pain
Pallor
Pulselessness
Paralysis
Paraesthesia
Perishingly cold
Hodgkin’s lymphoma classification A: Asymptomatic
B: Bad
Lichen planus characteristics Planus has 4 P‘s:
Peripheral
Polygonal
Pruritus
Purple
Hypertension: secondary hypertension causes CHAPS:
Cushing’s syndrome
Hyperaldosteronism [aka Conn’s syndrome]
Aorta coarctation
Phaeochromocytoma
Stenosis of renal arteries
· Note: only 5% of hypertension cases are secondary, rest are primary.
Hepatomegaly: 3 common causes, 3 rarer causes Common are 3
C’s:
Cirrhosis
Carcinoma
Cardiac failure
Rarer are 3 C’s:
Cholestasis
Cysts
Cellular infiltration
MI: sequence of elevated enzymes after MI “C–AST–Le”
(castle):
CK-MB first
AST second
LDH third
· Also: can use the last ‘E’ for ESR.
Pulmonary embolism: risk factors TOM SCHREPFER:
Trauma
Obesity
Malignancy
Surgery
Cardiac disease
Hospitalization
Rest [bed-ridden]
Elderly
Past history
Fracture
Estrogen [pregnancy, post-partum]
Road trip
TB: features TB is characterised by 4 C’s:
Caseation
Calcification
Cavitation
Cicatrization
Gallstones/cholecystitis: risk factors 5 F’s:
Fat
Female
Family history
Fertile
Forty
Rheumatoid arthritis: features RHEUMATOID:
Ragocytes/ Rheumatoid factor (anti-IgG)
HLA-DR4/ HLA-Dw4
ESR increase/ Extra-articular features (restrictive lung disease,
subcutaneous nodules)
Ulnar deviation
Morning stiffness/ MCP joint
Ankylosis/ Atlantoaxial joint subluxation/ Autoimmune/ ANA
T-cells (CD4)/ TNF
Osteopenia
Inflammatory synovial tissue/ Idiopathic/ IL-1
Deformities (swan-neck, boutonniere)
Neuroblastoma: features N-MYC:
Nuclei have “double minutes”
Malignant
Young
Catecholamine secreting
· And hallmark is n-mycamplification.
Lou Gehrig’s is both upper and lower motor neuron signs LoU
= Lower & Upper.
Dandy-Walker syndrome: components “Dandy Walker
Syndrome”:
Dilated 4th ventricle
Water on the brain
Small vermis
Cerebral palsy: general features PALSY:
Paresis
Ataxia
Lagging motor development
Spasticity
Young
Von Hippel-Lindau: signs and symptoms HIPPEL:
Hemanigoblastomas
Increased renal cancer
Pheochromocytoma
Port-wine stains
Eye dysfunction
Liver, pancreas, kidney cysts
· Bare bones version: Hippel-Lindau, with H and L as above.
Bronchial obstruction: consequences APPLE BABE:
Atelectasis
Pleural adhesions
Pleuritis
Lipid pneumonia
Effusion->organisation->fibrosis
Bronchiectasis
Abscess
Broncho and lobar pneumonia
Emphysema
Marble bone disease: signs and symptoms MARBLES:
Multiple fractures
Anemia
Restricted cranial nerves
Blind & deaf
Liver enlarged
Erlenmeyer flask deformity
Splenomegaly
· Eponymous name: Marbles = Albers-Schonberg (anagram).
Heart failure causes “HEART MAy DIE”:
Hypertension
Embolism
Anemia
Rheumatic heart disease
Thyrotoxicosis (incl. pregnancy)
Myocardial infarct
Arrythmia
Y
Diet & lifestyle
Infection
Endocarditis
Renal failure: causes AVID GUT:
Acute tubular necrosis
Vascular obstruction
Infection
Diffuse intravascular coagulation
Glomerular disease
Urinary obstruction
Tubulointerstitial nephritis
Multiple endocrine neoplasia III: components MEN
III is a disease of 3 M‘s:
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
Medulla of adrenal (pheochromocytoma)
Mucosal neuroma
Ulcerative colitis: features ULCERATIONS:
Ulcers
Large intestine
Carcinoma [risk]
Extraintestinal manifestations
Remnants of old ulcers [pseudopolyps]
Abscesses in crypts
Toxic megacolon [risk]
Inflamed, red, granular mucosa
Originates at rectum
Neutrophil invasion
Stools bloody
Virchow’s triad (venous thrombosis) “VIRchow”:
Vascular trauma
Increased coagulability
Reduced blood flow (stasis)
Pyrogenic meningitis: likeliest bug in age group “Explaining
Hot Neck Stiffness”:
· In order from birth to death:
E. coli [infants]
Haemophilus influenzae [older infants, kids]
Neisseria meningitis [young adults]
Streptococcus pneumoniae [old folks]
Endometrial carcinoma: risk factors ENDOMET:
Elderly
Nulliparity
Diabetes
Obesity
Menstrual irregularity
Estrogen therapy
hyperTension
Polycystic ovary: morphology, presentation · Morphology is
poly-C:
Cysts
Capsule thickened
Cortical stromal fibrosis
· Clinical presentation is OVARY:
Obese
Virilism or hirsutism
Amenorrhoea
Reproductive problem [infertile]
Young woman
Parkinson’s disease: symptoms PQRST:
Paucity of expression
parQinson
Rigidity (cogwheel)
Stooped posture
Tremor at rest
· If can’t remember that Parkinson’s tremor is the one that is “resting tremor”,
look at the last 3 letters: RST.
Kawasaki disease: features Disease name: a Kawasaki
motorcycle.
Usually young children, epidemic in Japan: Japanese child rides the motorcycle.
Conjunctival, oral erythema: red eyes, mouth.
Fever: thermometer.
Erythema of palms, soles: red palms, soles.
Generalized rash: rash dots.
Cervical lymphadenitis: enlarged cervical nodes with inflammation arrows.
Vasculitis of arteries: inflammation arrows on arteries.
Cardiovascular sequelae [20%]: inflammation arrows on cardiac arteries.
Treat with aspirin: aspirin headlight.
Interstitial lung disease: causes SARCOIDI:
Sarcoidosis
Allergic reaction
Radiation
Connective tissue disease
Occupational exposure
Infection
Drugs
Idiopathic
Herpes I and II: lab findings. She’s an odd chick: whenever
she’s in a restaurant, she always orders Her Peas and Cow
dry.
Herpes I and II have CowdryType A inclusion bodies
Emphysema: types, most important feature of each “Cigarettes
Is Primary Problem”:
· Types:
Centrilobular
Irregular
Pancinar
Paraseptal
· Most important feature for each type (in order as above):
Cigarrettes
Inflammation healed to scar
Protease inhibitor deficiency (a1-antitrypsin)
Pneumothorax
· “Cigarettes is primary problem” used since cigarettes is most common cause of
emphysema.
· Keeping P’s straight: Pan is antitrypsin.
Calcification: metastatic vs. dystrophic Metastatic:
Metabolism imbalance.
Dystrophic: Damaged tissue.
Haemochromatosis definition, classic triad “Iron man triathalon”:
Iron man: deposition of iron in many body tissues.
· Triathalon has 3 components, which match triad:
Swimming: Skin pigmentation
Biking: Bronze diabetes
Marathon: Micronodular pigment cirrhosis
COPD: 4 types and hallmark ABCDE:
Asthma
Brochiectasis
Chronic bronchitis
Dyspnea [hallmark of group]
Emphysema
· Alternatively: replace Dyspnea with Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio.
MEN I (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia) syndrome: components “Please
Please Pay Attention To peptic ulceration,
you worms“:
· Adenomas of:
Pituatary
Pancreatic islets
Parathyroid
Adrenal cortex
Thyroid, associated with peptic ulceration
· Syndrome is called “Wermer’s syndrome”.
Lung cancer: presentation ABCDE:
Snowball turned to Avalanche
Blood: hemoptysis
Cough
Distruption to airway in bronchus–>pneumonia
whEEzing
Deep venous thrombosis: diagnosis DVT:
Dilated superficial veins/ Discoloration/ Doppler
ultrasound
Venography is gold standard
Tenderness of Thigh and calf
Addison’s disease: features ADDISON:
Autoimmune
DIC (meningcoccus)
Destruction by cancer, infection, vascular insufficiency
Iatrogenic
Sarcoidosis, granulomatous such as TB histiomycosis
hypOtension/ hypOnatermia
Nelson’s syndrome [post adrelectomy, increased ACTH]
Breast cancer: risk assessment “Risk can be assessed by
History ALONE“:
History (family, previous episode)
Abortion/ Age (old)
Late menopause
Obesity
Nulliparity
Early menarche
McArdle’s syndrome MCARDLES:
Myoglobinuria
Cramping after exercise
Accumulated glycogen
Recessive inheritance
Deficiency of muscle phosphorylase
Lactate levels fail to rise
Elevated creatine kinase
Skeletal muscle only
Respiratory distress syndrome in infants: major risk factors
PCD (Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia, a cause of Respiratory distress
syndrome):
Prematurity
Cesarean section
Diabetic mother
Deep venous thrombosis: genetic causes ALASCA:
Antithrombin III
Leiden (Factor V)
APC (Activated Protein C)
S-protein deficiency
C-protein deficiency
Antiphospholipid antibody
Carcinomas having tendency to metastasize to bone “Particular
Tumours Love Killing Bone”:
Prostate
Thyroid
Lung
Kidney
Breast
Cushing syndrome CUSHING:
Central obesity/ Cervical fat pads/ Collagen fiber
weakness/ Comedones (acne)
Urinary free corisol and glucose increase
Striae/ Suppressed immunity
Hypercortisolism/ Hypertension/ Hyperglycemia/ Hirsutism
Iatrogenic (Increased administration of corticosteroids)
Noniatrogenic (Neoplasms)
Glucose intolerance/ Growth retardation
Apoptosis vs. necrosis “LIFELESS” (since cells are
dead):
· Differences are in:
Leaky membranes
Inflammatory response
Fate
Extent
Laddering
Energy dependent
Swell or shrink
Stimulus
Diabetic ketoacidosis: I vs. II ketONE bodies are
seen in type ONEdiabetes.
Baldness risk factors “Daddy Doesn’t Deny
Getting Hair Implants”:
Diet
Disease
Drugs
Genes
Hormones
Injury to the scalp
Tabes Dorsalis morphology DORSALIS:
Dorsal column degeneration
Orthopedic pain (Charcot joints)
Reflexes decreased (deep tendon)
Shooting pain
Argyll-Robertson pupils
Locomotor ataxia
Impaired proprioception
Syphilis
Buerger’s disease features “burger SCRAPS“:
Segmenting thrombosing vasculitis
Claudication (intermittent)
Raynaud’s phenomenon
Associated with smoking
Pain, even at rest
Superficial nodular phlebitis
· Alternatively, if hungry for more detail [sic], “CRISP PIG burgers“:
Chronic ulceration
Raynaud’s phenomenon
Intermittent claudication
Segmenting, thrombosing vasculitis
Pain, even at rest
Phlebitis (superficial nodular)
Idiopathic
Gangrene
PKU findings PKU:
Pale hair, skin
Krazy (neurological abnormalities)
Unpleasant smell
Atherosclerosis risk factors SHIFT MAID:
Smoking
Hypertension
(N)IDDM
Family history
Triglycerdides & fats
Male
Age
Inactivity
Diet / Drink
Parkinsonism: essential features TRAPS:
Tremor (resting tremor)
Rigidity
Akinesia
Postural changes (stooped)
Stare (serpentine stare)
· To remember what kind of tremor and postural change, can look at letter that
follows in TRAPS: Tremor is Resting, Posture is Stooped.
Thrombus: possible fates DOPE:
Dissolution
Organization & repair
Propagation
Embolization
Turner syndrome: components CLOWNS:
Cardiac abnormalities (specifically Coartication)
Lymphoedema
Ovaries underdeveloped (causing sterility, amenorrhea)
Webbed neck
Nipples widely spaced
Short
MI: sequence of elevated enzymes after MI “Time to
CALL 911″:
· From first to appear to last:
Troponin
CK-MB
AST
LDH1
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: symptom triad “PET WASP”:
Pyrogenic infections
Eczema
Thrombocytopenia
· WASP is the name of the causitive agent: Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein.
· Alternatively: Wiskott=Hot, Aldrich=Itch, Syndrom=Throm.
Sarcoidosis summarized SARCOIDOISIS:
Schaumann calcifications
Asteroid bodies/ [ACE] increase/ Anergy
Respiratory complications/ Renal calculi/ Restrictive lung
disease/ Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Calcium increase in serum and urine/ CD4 helper cells
Ocular lesions
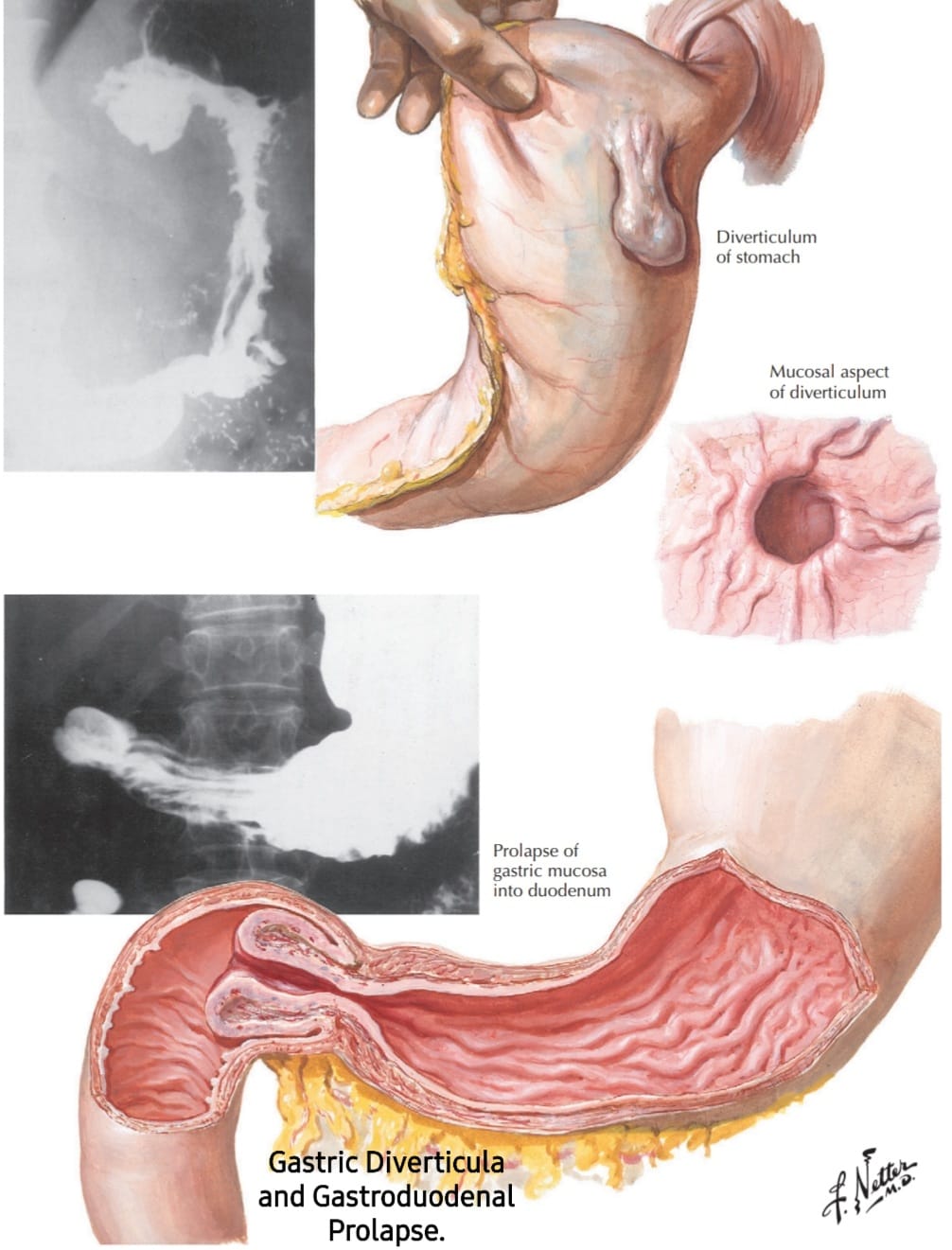
Gastric Diverticula and Gastroduodenal Prolapse
𝗚𝗮𝘀𝘁𝗿𝗶𝗰 𝗱𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘁𝗶𝗰𝘂𝗹𝗮 are rare and are found in 0.02% of autopsy specimens. Almost all are located on the posterior wall...



Discussion about this post