- Adductor pollicis palsy
- Opponens pollicis palsy
- Lateral 3 finger sensory palsy
- 1st and 2nd lumbrical palsy
Correct Answer : Adductor pollicis palsy
Ref: BDC 4th ed/ vol I p.113
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by the compression of Median nerve running deep to the flexor retinaculum in the wrist. Adductor pollicis is supplied by the ulnar nerve, which passes superficial to flexor retinaculum.
Structures passing superficial to flexor retinaculum
1) Palmar cutaneous branch of median nerve
2) Palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve
3) Ulnar nerve
4) Ulnar artery
5) Flexor carpi ulnaris
6) Palmaris longus tendon
7) Superficial branch of radial artery
Structures passing deep to flexor retinaculum
1) Median nerve
2) Radial and ulnar bursa
3) Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
4) Flexor digitorum profundus tendon
5) Flexor pollicis longus
6) Flexor carpi radialis
Nerve supply of muscles of hand
1) Median nerve
1st and 2nd lumbricals
Thenar muscles – Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens pollicis
Sensory- Palmar/ Anterior-Tip of index finger,
Lateral 3 ½ digits,
thenar area(lateral 2/3rd palm)
Posterior– lateral ½ palm
Proximal phalanx -lateral 2 ½ digits
Middle and distal phalanx – lateral 3 ½ digits
2) Ulnar nerve
3rd and 4th lumbricals
Interossei (palmar and dorsal)
Thenar muscles – Adductor pollicis, deep head of flexor pollicis brevis
Hypothenar muscles – Palmaris brevis
Flexor digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Opponens digiti minimi
Sensory- Palmar/ Anterior -Tip of little finger
Hypothenar area (medial 1/3rd palm)
Medial 1 ½ digits
Posterior– Medial ½ palm
Proximal phalanx – medial 2 ½ digits
Middle and distal phalanx- medial 1 ½ digits
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by the compression of Median nerve running deep to the flexor retinaculum in the wrist. Adductor pollicis is supplied by the ulnar nerve, which passes superficial to flexor retinaculum.
Structures passing superficial to flexor retinaculum
1) Palmar cutaneous branch of median nerve
2) Palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve
3) Ulnar nerve
4) Ulnar artery
5) Flexor carpi ulnaris
6) Palmaris longus tendon
7) Superficial branch of radial artery
Structures passing deep to flexor retinaculum
1) Median nerve
2) Radial and ulnar bursa
3) Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon
4) Flexor digitorum profundus tendon
5) Flexor pollicis longus
6) Flexor carpi radialis
Nerve supply of muscles of hand
1) Median nerve
1st and 2nd lumbricals
Thenar muscles – Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens pollicis
Sensory- Palmar/ Anterior-Tip of index finger,
Lateral 3 ½ digits,
thenar area(lateral 2/3rd palm)
Posterior– lateral ½ palm
Proximal phalanx -lateral 2 ½ digits
Middle and distal phalanx – lateral 3 ½ digits
2) Ulnar nerve
3rd and 4th lumbricals
Interossei (palmar and dorsal)
Thenar muscles – Adductor pollicis, deep head of flexor pollicis brevis
Hypothenar muscles – Palmaris brevis
Flexor digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Opponens digiti minimi
Sensory- Palmar/ Anterior -Tip of little finger
Hypothenar area (medial 1/3rd palm)
Medial 1 ½ digits
Posterior– Medial ½ palm
Proximal phalanx – medial 2 ½ digits
Middle and distal phalanx- medial 1 ½ digits

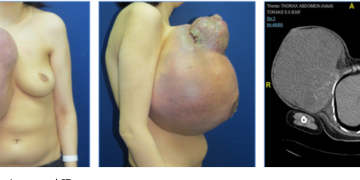


Discussion about this post