Medical Study
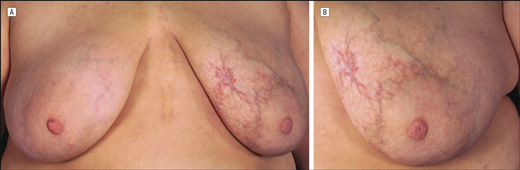
Diffuse Dermal Angiomatosis of the Breast
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is rare and usually considered a variant of reactive angioendotheliomatosis. It generally involves the extremities of patients with severe vascular disease and other comorbidities. Two patients with breast involvement have been described; however, neither had a relevant medical history or a vaso-occlusive disorder, but both had large pendulous breasts, and 1 was…

Bodies in diseases – MBBS Pathology Study Notes
Listing out the pathology notes for the MBBS students. this note is about the Important bodies in pathology in various diseases and conditions::
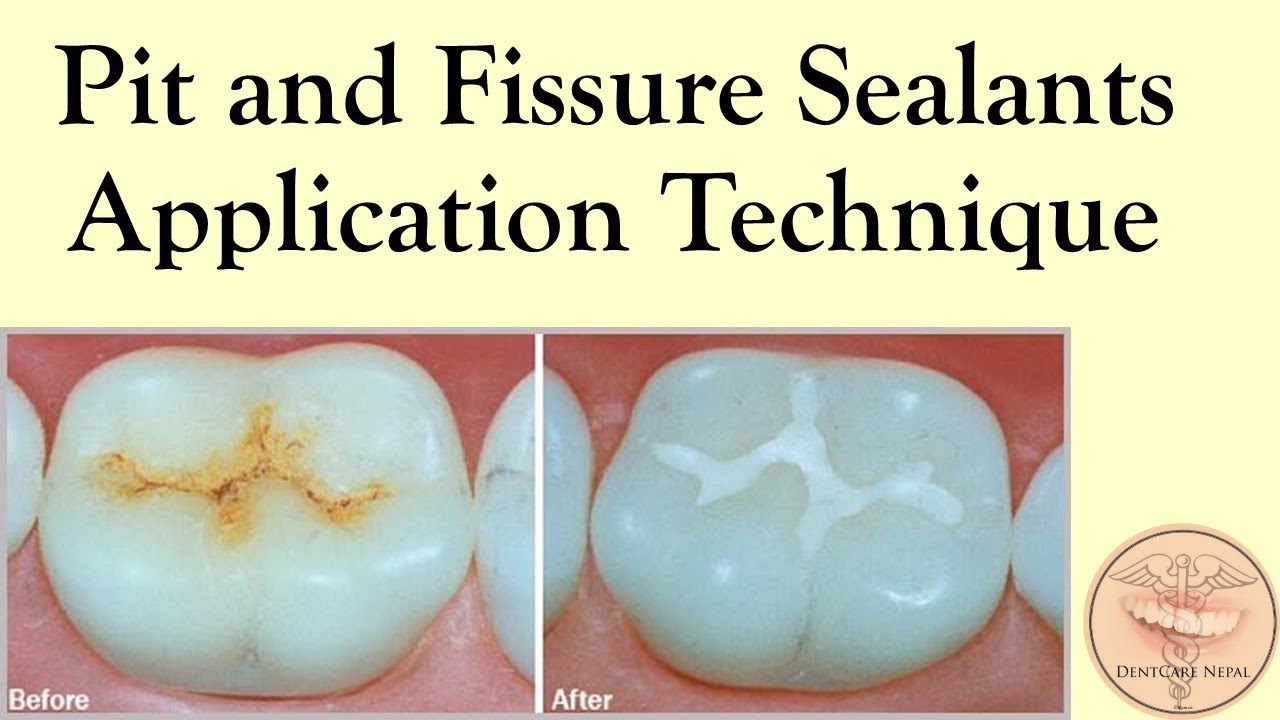
Pit and Fissure Sealants: A Recent Advancement
The term pit and fissure sealant (PFS) is used to describea material, i.e., introduced into the occlusal pits and fissures of caries-susceptible teeth, thus forming a micromechanically bonded, protective layer cutting access ofcaries producing bacteria from their source of nutrients.1Buonocore’s classic study of 1955 marked the startof a major revolution in the clinical practice of…
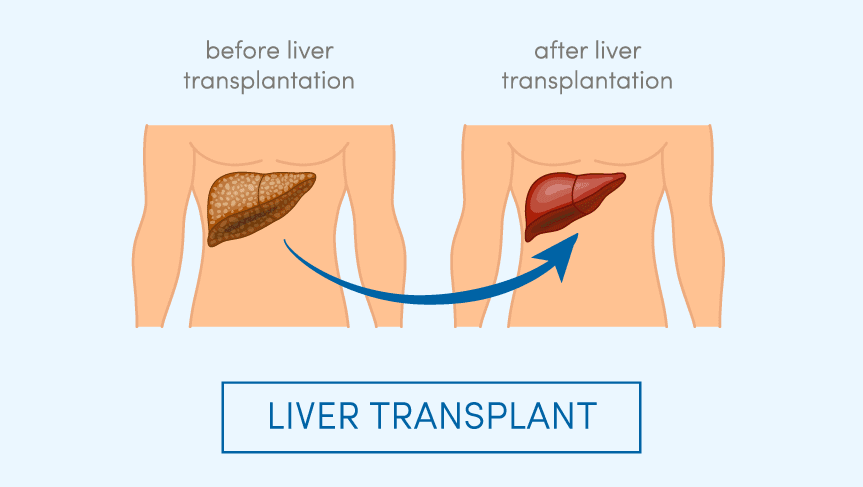
Liver transplantation – acute liver failure – end-stage liver disease
Liver transplantation (LT) is indicated for the treatment of acute liver failure (ALF) and end-stage liver disease (ESLD). Currently, the overall 1-year and 5-year post-LT patient survival rates are 80-90% and 60-75%, respectively. Liver transplantation can be classified according to the type of donor, into deceased and live donor liver transplants. Liver grafts in the Western countries come predominantly from deceased donors in around 95% of the cases*. Orthotopic…
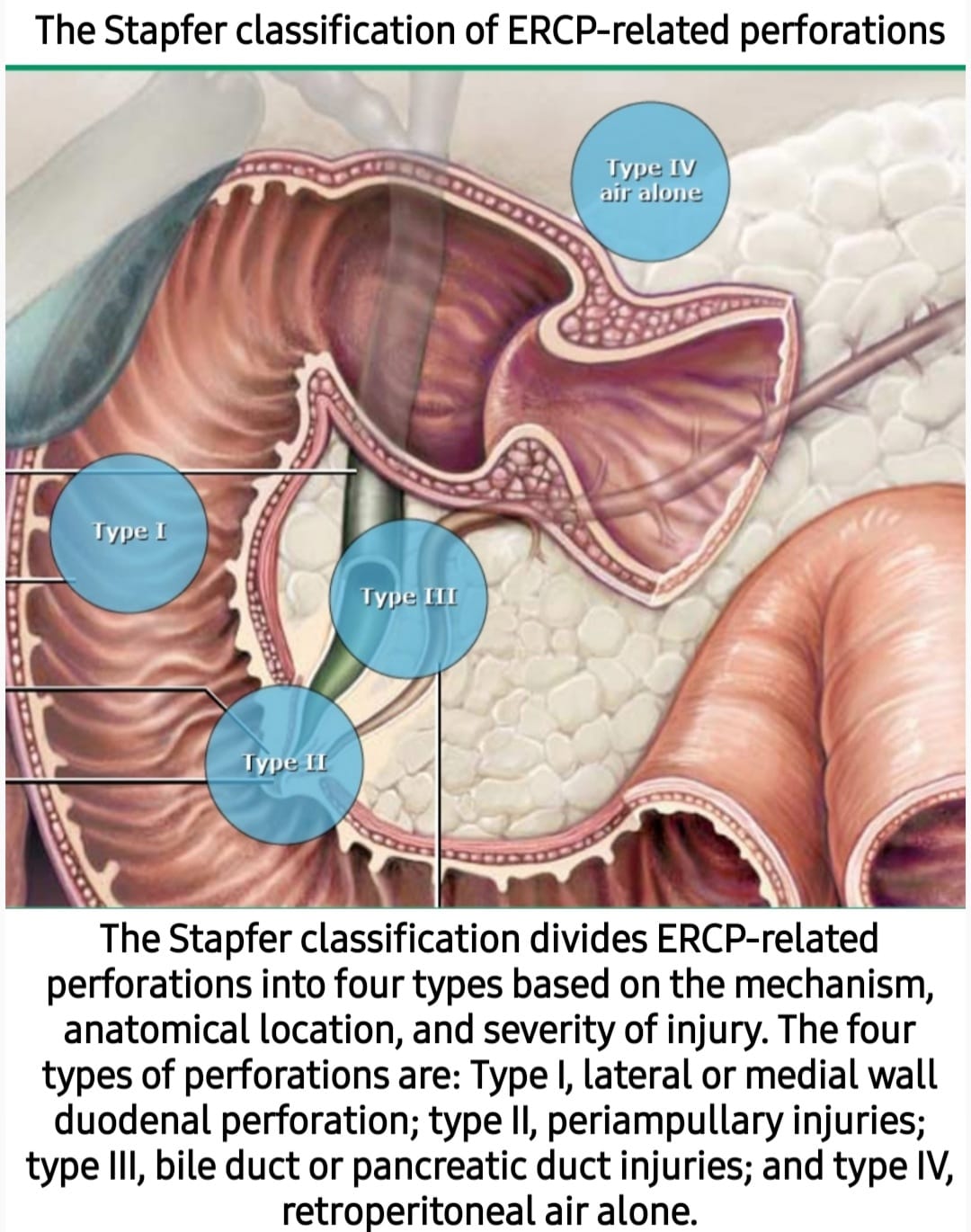
𝗦𝘁𝗮𝗽𝗳𝗲𝗿 𝗰𝗹𝗮𝘀𝘀𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗼𝗳 𝗘𝗥𝗖𝗣 𝗶𝗻𝗷𝘂𝗿𝘆 𝗼𝗳 𝗱𝘂𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗻𝘂𝗺/𝗖𝗕𝗗/𝗔𝗺𝘂𝗽𝗹𝗹𝗮:
Stapfer type 𝗜 are free bowel wall perforations, usually from the endoscope, and these tend to be larger and require immediate operative repair. •Type 𝗜𝗜 are retroperitoneal duodenal perforations and are secondary to periampullary injury. These are the most commonly encountered type of perforation and require surgical intervention depending on severity. •Type 𝗜𝗜𝗜 perforations involve…










