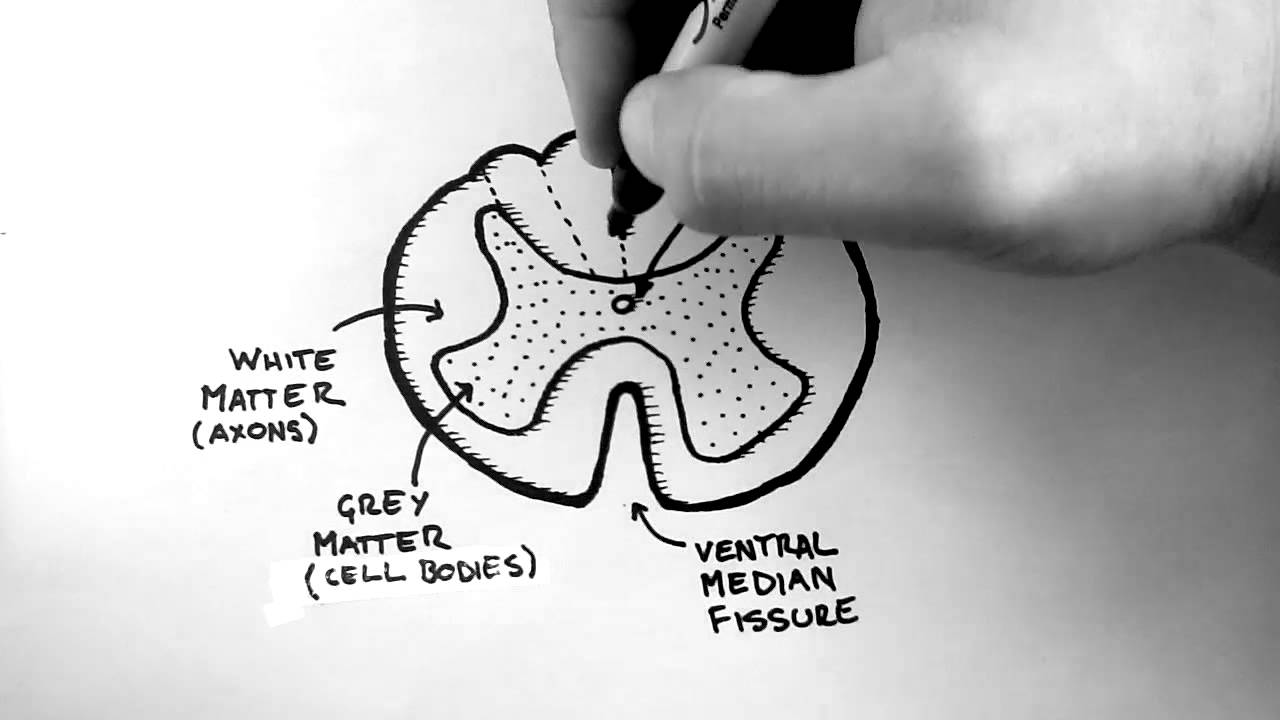
General Pathology Revision questions for Exam part 1 .

These exam points are useful for for the NMCLE, USMLE, FCPS, and many other medical exam
Answer or Keys are at the end for General Pathology Revision questions for Exam one .
1. Leading cause of death due to poisoning?
2. CO poisoning inhibit which enzyme?
3. Name mitochondrial toxins ?
4. Most susceptible to hypoxia in nephron?
5. Irreversible damage to neuron occurs after —– minutes of global hypoxia?
6. Most destructive free radicals?
7. Which vitamin is the best neutralizer of free radical?
8. Marker of intermediate filament degradation?
9. Mallory bodies are present in ?
10. Acetaminophen free radicals are formed in?
11. Wear and tear pigment?
12. Hemosedrin laden macrophages present in left sides heart failure are called?
13. What is called green bile ?
14. Disordered cell growth is calle ?
15. Examples of permanent cells?
16. Most common cause of caseous necrosis?
17. Programmed cell death is called?
18. Guardian of genome is?
19. Which is specific for pancreatitis?
20. Heterophagy is seen in which cell organelle?
21. Cerebral infarct is example of?
22. What is called red bile?
23. Extrinsic pathway in apoptosis require?
24. In lead poisoning lead deposits in?
25. Only endogenous pigment?
26. Which metaplasia occurs in brain?
27. Most susceptible zone in hypoxia of hepatocyte ?
28. Oxidase reaction produce which radicals?
29. Primary lysosomes are derived from ?
30. Lewy body seen in ?
31. Most common cause of tissues hypoxia?
32. Most common site for metastatic calcification? Kidney
33. Vitamin as an antioxidant?
34. Central organ in apoptosis?
35. Caspases are involved in which phenomenon?
36. Female had silicon breast implant which was then removed , wich cells would be numerous ?
37. Omental necrosis is of which type?
38. Superimposed infection on necrosis is called ?
39. Metaplasia of surface epithelium most commonly causes by?
40. In our country the most common cause of cell injury is ?
41. Immediate affect after injury to a vessel is ?
41. Major circulating phagocyte?
42. Most important chemical mediator of inflammation?
43. Clearance of neutrophils in acute inflammation is by?
44. Neutrophil leucocytosis is caused by?
45. The hallmark of acute inflammation is increased ?
46. Acute phase reactants mostly synthesized in?
47. Most common cause of skin abscess?
48. Hall mark of chronic inflammation?
49. Kininogen converts into bradykinin due to?
50. Prostaglandin that helps in protection of gastrointestinal mucosa is??
51. Prostacyclin is produced by?
52. Fever in inflammation is caused by ?
53. ICAM and VCAM are responsible for ?
54. Most common cause of increases permeability?
55. Chemotaxis is a feature of ?
56. Most common cause of hyperkalemia?
57. Virchows triad?
58. Pulmonary thromboembolism originate from?
59. Best indicator of tissues hypoxia?
60. Most common cause of respiratory acidosis ?
61. Cushing triad?
62.most common manifestation of septic patient is ?
63. Most important distinguishing feature if hypo volumic and septic shock is ?
64. Last mediator of endo toxic shock ?
65. Death due to embolism after accident ?
66. Severe generalized Edema is called ?
67. Which vitamin involved in synthesis of collagen?
68. Keyloid is excess of which type of collagen?
69. Corticosteroid inc which wbc?
70. The hallmark of healing?
71. The element act as cofactor in collagen synthesis is?
72. Polyclonal gammopathy is sign of ?
73. The liver contain stem cells in?
74. Most important cells for wound contraction is?
75. Resistance to tension in main function of which collagen?
76. Liver regenerates in how many days?
77. Most common cause of impaired wound healing?
78. Cells increasing in number
Is called?
79. Grading of tumor is done by?
80. Sarcoma involves which origin?
81. Down syndrome is associated with which malignancy?
82. Most common metastatic cancer to bone?
83. Barrets esophagous associated with ?
84. Bcl-2 gene associated with which tumor ?
85. Ret gene associated with which tumor?
86. Li fraumani syndrome associated with which gene?
87. Colorectal carcinoma associated with which gene?
88. TRAP is tumor marker of?
89. S-100 tumor marker of?
90. Calcitonin tumor marker of?
91. Disease associated with asbestosis?
92. Vinyl chloride associated with which disease ?
93. ACTH like peptide are secreted by which tumor?
94. Name disease associated with Psamomma bodies?
95. Most common site of metastasis ?
96. Most common cancer related death?
97. Alkylating agents associated with which malignancy?
98. Polycythemia is associated with which carcinoma?
99. CA-125 tumor marker of ?
100. HTLV-1 virus associated cancer is?
General Pathology Revision questions for Exam Part 2
KEYS
1. CO poisoning
2. Cytochrome oxidase.
3. Alcohol and salicylate
4. Proximal tubule
5. 5 min
6. Hydroxyl free radicals
7. Vit C
8. Ubiquitine
9. Alcoholic liver disease
10. Liver
11. Lipofuschin
12. Heart failure cells
13. Biliverdin
14. Dysplasia
15. Neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
16. TB
17. Apoptosis
18. P53
19. Lipase
20. Lysosomes
21. Liquifactve infarct
22. Bilirubin
23. TNF
24. Proximal renal tubule
25. Melanin
26. No metaplasia occurs in brain
27. Zone 3
28. Superoxide free radicals
29. Golgi apparatus
30. Idiopathic parkinson disease
31. Ischemia
32. Kidney
33. Vit E
34. Mitochondria
35. Apoptosis
36. Plasma cells
37. Fat necrosis
38. Wet gangrene
39. Chronic irritation.
40. Ischemia
41. Vasoconstriction
41. Neutrophil
42. Histamine
43. Apoptosis
44. Catecholamines , corticosteroids and lithium
45. Vascular permeability.
46. Liver
47. Staph aureus
48. Tissue destruction
49. Hageman factor
50. PGE2
51. Endothelial cells
52. IL1 and TNF-a
53. Leukocyte adhesion
54. Inflammation
55. Acute inflammation
56. Renal failure
57. Endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow and hypercoagubility
58. Femoral vein
59. Mixed venous O2
60. Anxiety
61. Inc bp, HTN, bradycardia
62. Hypotension
63. Temperature
64. IL6
65. Fat embolism
66. Anasarca
67. Vit c
68. Type 3
69. Neutrophils
70. Granulation tissue
71. Zinc
72. Chronic inflammation
73. Canal of hering
74. Myocibroblasts
75. Type 1 collagen
76. 10-14 days
77. Infections
78. Hyperplasia
79. Degree of cellular differentiation on histological appearance
80. Mesenchymal
81. ALL
82. Breast
83. Esophageal adenocarcinoma
84. Follicular lymphoma
85. MEN IIA and IIB
86. P53
87. APC
88. Hairy cell leukemia
89. Melanoma, astrocytoma
90. Thyroid medullary carcinoma
91. Mesothelioma and Bronchogenic carcinoma
92. Angiosarcoma
93. Small cell lung carcinoma
94. Papillary ca of thorid, serous papillary cystadebocarcinoma of ovary, meningioma,
malignant mesothelioma
95. Lymph nodes
96. Lung carcinoma
97. Leukemia
98. RCC
99. Ovarian carcinoma
100.Adult T cell leukemia/ lymphoma