Effective Management And treatment of bells palsy by Shristi Shakya, MPT (Masters in physiotherapy), Neurological and Psychosomatic Disorders. we will be discussing the treatment of bells palsy which leads to faster bell’s palsy recovery.
Management And treatment of bells palsy
Introduction: what is bells palsy?
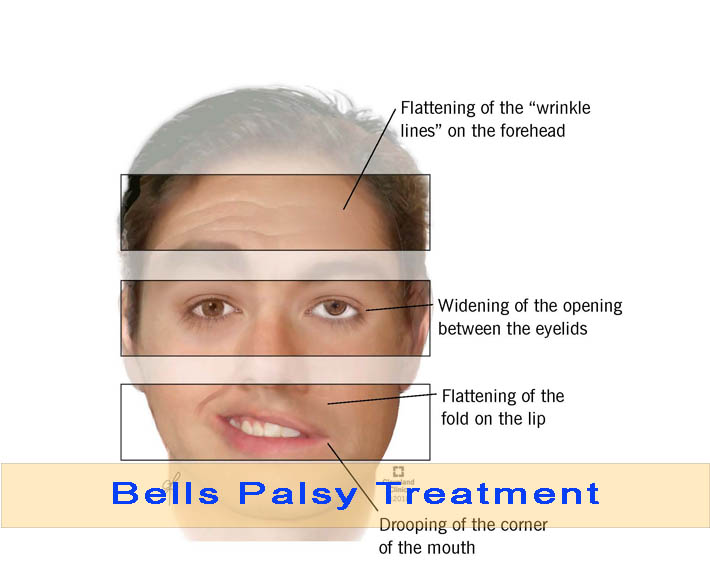
Paralysis of one side of the face you ever have noticed. This happens unknowingly and suddenly. this is bells palsy . Bell’s Palsy is a lower motor neuron kind of facial paralysis, wherein one side of the face of an individual is paralyzed, causing drooping of one side of the face, owing to the trauma to the 7th cranial nerve, i.e. the facial nerve.
It is acute on onset presumed to be due to non-suppurative inflammation of unknown etiology.
Etiology and Risk Factors and Incidence of bells palsy
In order to know the Effective Management And treatment of bells palsy, we should about its etiology and risk factors . We already know that its due to problems in the facial nerve which can be due to the following reasons.
Etiology of Bells Palsy
- Herpes zoster infection.
- History of exposure of ear to extreme cold.
- History of drinking excessive cold drinks or ice cream.
- Upper Respiratory Tract infection.
- Reactivated Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1) infection.
- Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV).
- Water retention during pregnancy.
Risk Factors:
- Immunocompromised Individual.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
- Sarcoidosis
- Lyme Disease.
- Ebstein Barr Virus (EBV).
- Comorbid Individuals,
Incidence:
- It affects males and females equally.
- It can occur at any age group from infancy to old age but has a slightly higher incidence in mid and later life.
- found Higher in pregnancy.
- Following Viral Upper Respiratory Tract infection.
- In immunocompromised individuals with comorbidities.
Signs and Symptoms in bells palsy
The bells palsy symptoms are due to majorly the muscles of facial expressions. Emotional and associated movements will be involved due to:
- Paralysis of one side of the face.
- Absence of Frowning of the forehead.
- Drooping of the corner of the mouth.
- Smoothening of the Creases and Skinfold of the face.
- Difficulty in closing the eye completely.
- Pain at the ear, mastoid region, angle of jaw during the onset.
- Temporal headache – which can be a warning sign.
- Excessive salivation.
- Decreased lacrimation.
- Heaviness or numbness of the face.
- Accumulation of food between the teeth and cheek.
- Difficulty in blowing and pursing the lips.
- Loss of taste sensation.
Complications of bells palsy
- Motor Synkinesis/associated movements.
- Crocodile tears.
- Reduction of taste sensation.
Investigations for bells palsy
Different investigations for bells palsy are done. They are done in order to find out any problem in the pathway of the nerve.
- Strength Duration Curve (SDC).
- Electromyography (EMG).
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCV).
Grading of bells palsy
Regarding the grading of bells palsy, most of the common gauzing tool for Bell’s Palsy are:
- House Brackmann Scale.
- Sunnybrook Scale/Facial Nerve Grading Scale.
Management and treatment of bells palsy
The management and treatment for bells palsy would be medical management and physiotherapeutic Management. The bell’s palsy recovery may be slow but will be good as both medical and physiotherapy management started as soon as possible. They are briefly described below.
Medical Management:
- Corticosteroids (Prednisolone).
- Antiviral Drugs.
- Combination Therapy; a combination of both corticosteroids and antiviral drugs.
Physiotherapeutic Management:
for the treatment of bells palsy and early recovery of bells palsy, physiotherapy with medical management is effective. This physiotherapeutic management for the following reasons.
- To resolve inflammation:
- Short Wave Diathermy (SWD) or Infrared Ray Therapy (IRR) at the stylomastoid foramen to increase the blood circulation.
- To maintain muscle properties:
- Interrupted Galvanic Stimulation to the paralyzed muscles followed by Surged Faradic Stimulation to the facial nerve trunk.
- Facial Massage:
- Towards upward direction to maintain blood circulation.
- Kabat’s technique is one of the most followed massage techniques to cure facial muscle paralysis.
- Taping/Splinting:
- To maintain the facial symmetry.
- Eye Care:
- Special care must be given to the eye since the patient won’t be voluntarily able to close his eye facilitating the entry of foreign bodies into the eye.
- Therefore, it is crucial to suggest them to wear protective goggles or an eye patch.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Prognosis can be gauzed with the help of the Strength Duration Curve (SDC).
- Re-education/Visual Feedback Exercises:
- bell’s palsy exercises are one of the important for fast bell’s palsy recovery
- It is very important to ask the patient to perform the exercise in front of the mirror, wherein s/he gets visual feedback and perform exercises more efficiently.
- The most commonly used re-educational technique is Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) techniques to the facial muscles.
- Eventually, when the muscle starts gaining its strength, exercises can be progressed to resisted one in order to further improve its strength.
- Oral Care:
- Strategic eating can help prevent the accumulation of food particles at the cheeks, which includes; usage of straw while drinking and preferring soft food to hard ones.
- Recent Advances:
- Mime Therapy/Neuromuscular Retraining
- Mental Imagery
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy(CBT)
- Miscellaneous:
- It is advisable to not drink excessively cold drink or ice cream is you are at the risk group.
- Always remember to cover your ears during long journeys to protect the gush of air entry into the ears, irritating the facial nerve.
Summary and conclusion
- Bell’s Palsy is a lower motor neuron type of facial paralysis of unknown cause. Early medical treatment is crucial for complete recovery. Combination therapy may be beneficial for Effective Management And treatment of bells palsy. Eye protection with lubrication and a patch is essential to prevent long-term complications.